According to Peter Piper, professor from Sheffield University, carbonated drinks contain a substance which harmful effects are still being underestimated.
Many of the problems that are associated with age-related changes or alcohol abuse, such as cirrhosis of the liver and Parkinson’s disease can be caused by usual soft drinks.
After spending a huge amount of time on experiments in his laboratory, Professor of Molecular Biology
Saturday, July 23, 2011
Lose Weight With Top 10 Healthy Drinks

When it comes to weight loss, substituting healthy drinks for those sugary sodas and energy drinks can have a drastic effect on your weight loss goals. Most people don’t realize how many calories they take in each day from drinks alone. For instance, a caffe mocha with all the fixings can pack in over 500 calories! So as
Thursday, July 21, 2011
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder (HD), is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea. It is much more common in people of Western European descent than in those of Asian or African ancestry. The disease is caused by an autosomal dominant mutation on either of an individual's two copies of a gene called Huntingtin, which means any child of an affected parent has a 50% risk of inheriting the disease. In the rare situations where both parents have an affected copy, the risk increases
Wednesday, July 20, 2011
HIV Disease
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease was first described in 1981 among 2 groups—one in San Francisco and the other in New York City. Numerous young homosexual men presented with opportunistic infections that, at the time, were typically associated with severe immune deficiency due to Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) or aggressive Kaposi sarcoma [1] The HIV virus itself was not identified for another 2 years[2] ; during that time, various other causes were considered, including lifestyle factors, chronic drug abuse, and other infectious agents.[3]
The HIV epidemic spread rapidly and silently in the absence of testing. However
The HIV epidemic spread rapidly and silently in the absence of testing. However
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a clinical syndrome produced by inflammation of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. In children, acute bronchitis usually occurs in association with viral respiratory tract infection. Acute bronchitis is rarely a primary bacterial infection in otherwise healthy children.
Examples of normal airway color and architecture and an airway in a patient with chronic bronchitis are shown below.
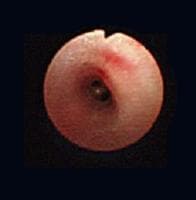 Normal airway color and architecture
Normal airway color and architecture
Examples of normal airway color and architecture and an airway in a patient with chronic bronchitis are shown below.
 Normal airway color and architecture
Normal airway color and architectureTheraphy HIV AIDS


DEFINITION
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a collection of symptoms of disease or abbreviation for acquired imune deficiency syndrome caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
HIV virus can be found in body fluids, especially in blood, semen, vaginal fluids, breast milk. The virus destroys the human immune system and may decrease or loss endurance, so easily affected by infectious diseases.
SYMPTOMS
A person who has been infected with HIV is likely to pas through three stages of the disease. Not all individuals experience all of the stages.
1. Acute Retroviral Syndrome
Acute retroviral syndrome is a term used describe a group of symtoms that can resemble mononucleosis. Mononucleosis is like a flu-like infection, include
Sjogren's Syndrome
Definition
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which immune cells attack and destroy the glands that produce tears and saliva. Sjögren's syndrome is also associated with rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. The hallmark symptoms of the disorder are dry mouth and dry eyes. In addition, Sjogren's syndrome may cause skin, nose, and vaginal dryness, and may affect other organs of the body including the kidneys, blood vessels, lungs, liver, pancreas, and brain.
It was found by Henrik Samuel Conrad Sjogren n 1933.
Sjögren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which immune cells attack and destroy the glands that produce tears and saliva. Sjögren's syndrome is also associated with rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. The hallmark symptoms of the disorder are dry mouth and dry eyes. In addition, Sjogren's syndrome may cause skin, nose, and vaginal dryness, and may affect other organs of the body including the kidneys, blood vessels, lungs, liver, pancreas, and brain.
It was found by Henrik Samuel Conrad Sjogren n 1933.
Etiology
Researchers think Sjogren's syndrome is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Several different genes appear to be involved, but scientists are not certain exactly which ones are linked to the disease since different genes seem to play a role in different people. For example, there is one gene that predisposes Caucasians to the disease. Other genes are linked to
Medical Treatment of Steven Johnson Syndrome (SJS)

Management
The management major is to stop the drug suspected as the cause of Steven Johnson Syndrome, morbidity and mortality would increase if the drug is a slow fuse to be avoided. The study says that low mortality rate in patients caused by medicines in a way immediately avoid the drug when it first appears the originator of the emergence of bull.
General Principles of Treatment SJS
In SJS patients first came to the place of service, the important thing to note on the treatment of SJS is in accordance with emergency care. First we must note the airway, breathing, balance hemodynamics, wound care and pain control, temperature control environment, maintenance of sterile field and aseptic handling, sterile, avoidance of various adhesive materials, maintenance of peripheral vein away from
Tuesday, July 19, 2011
RABIES
DEFINITION:
An acute infectious disease of warm-blooded animals characterized by involvement of the nervous system resulting in death.


ETIOLOGY
It is caused by the RABIES VIRUS, a rhabdovirus of the genus lyssavirus. RHABDOVIRUS: any group of rod-shaped RNA viruses with 1 important member, rabies virus, pathogenic to man. The virus has a predilection for tissue of mucus-secreting glands and the Central Nervous System. All warm-blooded animals are susceptible to infection with these viruses. LYSSAVIRUS: Greek – frenzy. A genus of the family Rhabdoviridae. There are 2 kinds of rabies. URBAN or CANINE RABIES are transmitted by dogs. SYLVATIC RABIES are transmitted from
Syphilis

Definition
Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease caused by the spirochaete Treponema pallidum. It progresses in stages. Syphilis is easy to cure in its early stages. But without treatment, it can hurt your body’s organs, leading to severe illness and even death.
Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease caused by the spirochaete Treponema pallidum. It progresses in stages. Syphilis is easy to cure in its early stages. But without treatment, it can hurt your body’s organs, leading to severe illness and even death.
Etiology
Syphilis caused by Treponema pallidum. Treponema pallidum including Spirochaeta group which is shaped like a spiral with a length between 50-20 microns wide and 0.1 to 0.2 microns, easily visible with dark field microscope looks like a spiral that can perform movements such as rotation. These organisms are easily killed by
Serology Diagnostic for Syphilis
Diagnosis of Syphilis
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on history, physical examination, and laboratory investigation. It is essential that the stage of syphilis be accurately assessed and documented in order to ensure appropriate management of cases and contacts.
Darkfield Microscopy & Direct or Indirect
1. Fluorescent Antibody Test (DFA/IFA):
Darkfield microscopy and DFA/IFA testing of lesion exudates or tissues are the definitive methods for diagnosing early syphilis when an active chancre, mucous patch, or condyloma latum is present. It is also useful for testing nasal discharge in a neonate with snuffles.
Darkfield microscopy is often not practical (it is not available in most labs including CPL) as it requires a skilled technician on-site. In addition, specimens must be appropriately collected and quickly examined within 5-20 minutes of collection. Positive tests on these materials for
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on history, physical examination, and laboratory investigation. It is essential that the stage of syphilis be accurately assessed and documented in order to ensure appropriate management of cases and contacts.
Darkfield Microscopy & Direct or Indirect
1. Fluorescent Antibody Test (DFA/IFA):
Darkfield microscopy and DFA/IFA testing of lesion exudates or tissues are the definitive methods for diagnosing early syphilis when an active chancre, mucous patch, or condyloma latum is present. It is also useful for testing nasal discharge in a neonate with snuffles.
Darkfield microscopy is often not practical (it is not available in most labs including CPL) as it requires a skilled technician on-site. In addition, specimens must be appropriately collected and quickly examined within 5-20 minutes of collection. Positive tests on these materials for
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria syndrome

Disease name and synonyms
• Progeria
• Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome
(HGPS)
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by many features reminiscent of marked premature ageing. The characteristic features include short stature, prominent eyes, micrognathia, craniofacial disproportion, loss of subcutaneous fat, alopecia, beaked nose, "plucked-bird" appearance, coax valga, pathologic bone fractures, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disorders. Other clinical features include abnormal and delayed dentition, thin and highpitched voice, pyriform thorax, and short dystrophic clavicles.
At birth, the appearance of patients with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is generally normal, but by the first year of age patients show severe growth retardation, balding and sclerodermatous skin changes. Affected children are usually short and thin with an average height of 100 cm or so and average weight of 12-15 kg or even less. Death usually occurs from 7 to 28 years, with a median age of 13.4 years. Over 80% of deaths are due to heart attacks or congestive heart failure.
Molecular Genetics
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is caused by mutation in the lamin A (LMNA) gene. Lamins are type V intermediate filament proteins and
NICOTINE ADDICTION
Nicotine Addiction
Addiction is defined as a situation in which a drug unreasonably controls behavior. The primary criteria for drug dependence are highly controlled or compulsive use of a drug with psychoactive effects and the presence of drug-reinforced behavior. Additional criteria are stereotypic patterns of use, use despite harmful consequences, relapse following abstinence, and recurrent drug cravings.
Addiction is defined as a situation in which a drug unreasonably controls behavior. The primary criteria for drug dependence are highly controlled or compulsive use of a drug with psychoactive effects and the presence of drug-reinforced behavior. Additional criteria are stereotypic patterns of use, use despite harmful consequences, relapse following abstinence, and recurrent drug cravings.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


